The E-Puck2 ARGoS Plug-in

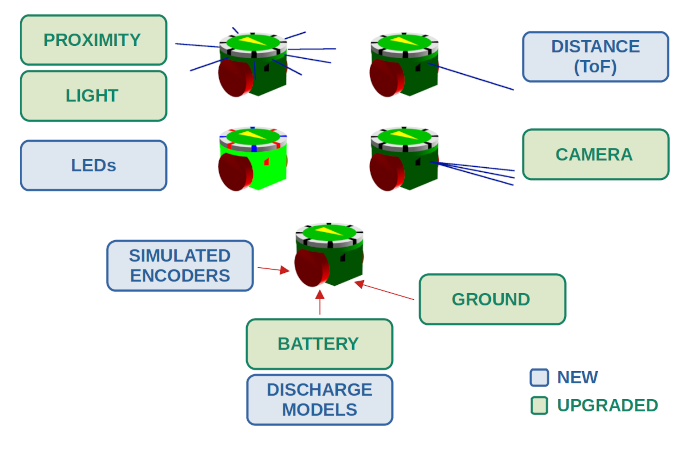
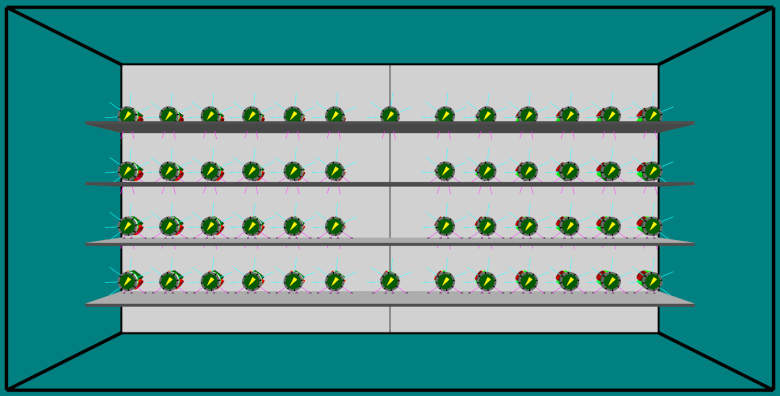
We present a new plug-in for the ARGoS swarm robotic simulator to implement the E-Puck2 robot model, including its graphical representation, sensors and actuators. We have based our development on the former E-Puck robot model (version 1) by upgrading the existing sensors (proximity, light, ground, camera, and battery) and adding new ones (time of flight and simulated encoders) implemented from scratch. We have adapted the values produced by the proximity, light and ground sensors, including the E-Puck2’s onboard camera according to its resolution, and proposed four new discharge models for the battery. We have evaluated this new plug-in in terms of accuracy and efficiency through comparisons with real robots and extensive simulations. In all our experiments the proposed plug-in has worked well showing high levels of accuracy. The observed increment of execution times when using the studied sensors varies according to the number of robots and types of sensors included in the simulation, ranging from a negligible impact to 53% longer simulations in the most demanding cases.
More about this in our Open Access article: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.robot.2023.104412
Plug-in available at: https://gitlab.com/uniluxembourg/snt/pcog/adars/e-puck2
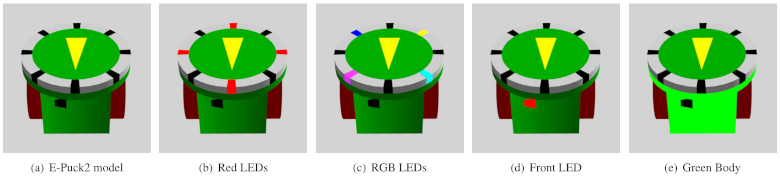
Robot Model
Available Sensors and Actuators
ARGoS Simulation
Publications:
Daniel H. Stolfi and Grégoire Danoy. Design and analysis of an E-Puck2 robot plug-in for the ARGoS simulator. In: Robotics and Autonomous Systems, vol. 164, pp. 104412, 2023.
doi> 10.1016/j.robot.2023.104412 | [BibTex] | [Files]@Article{Stolfi2023, author = {Daniel H. Stolfi and Gr\'{e}goire Danoy}, journal = {Robotics and Autonomous Systems}, title = {Design and analysis of an {E-Puck2} robot plug-in for the {ARGoS} simulator}, year = {2023}, issn = {0921-8890}, pages = {104412}, volume = {164}, doi = {10.1016/j.robot.2023.104412}, keywords = {E-puck2, ARGoS, Computer simulations, Sensors, Swarm robotic}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921889023000519}, }
This work is supported by the Luxembourg National Research Fund (FNR) - ADARS Project, ref. C20/IS/14762457. The experiments presented in this paper were carried out using the SwarmLab facility of the FSTM/DCS.